Changes in the Cervical Mucus After Implantation
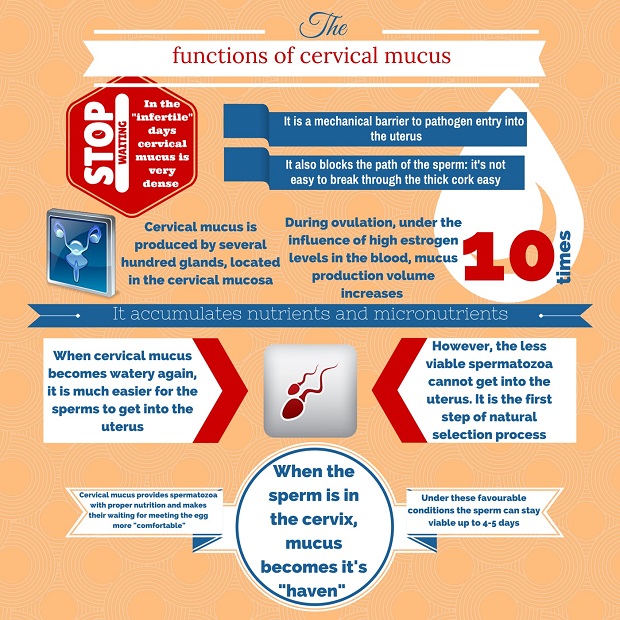
Cervical mucus is natural discharge from the uterine cervix. It contributes to fertilization. Mucus also mechanically protects the uterus from infections. During the regular menstrual cycle its consistency changes 5 times: “dry days”, sticky, cream-like, liquid and somewhat “egg white” discharge. The latter is most favorable for fertilization. After implantation cervical mucus undergoes changes on the biochemical level. Its amount and texture is quite individual for pregnant women.
Cervical mucus has the form of specific discharge from the uterine cervix, which contains a complex secrete from tubal, uterine and cervical glands. This fluid is vital for a woman’s fertility.
The natural purpose of cervical mucus is contributing to the meeting of the ovum and the sperm cell. It also performs the important function of mechanical protection of the internal genitalia from the penetration of bacterial infections through the pharyngeal cavity of the uterine cervix.
Cervical mucus flows outwards and is more intense along peripheral areas. Such a dynamics provides for natural elimination of weakened sperm cells. For those, who managed to get into the cervix, mucus serves a favorable nutritive environment. In such a surrounding the “bravehearts” can survive from three to five days, waiting for the detachment of the desired ovum. Fertilization is followed by implantation, which influences cervical mucus.
Cervical mucus during a regular cycle
The consistency and amount of cervical mucus vary throughout a regular menstrual cycle, depending on the hormone, which takes up the “ruling post” in the woman’s organism. It is a well-known fact, that a regular cycle covers 3 phases: follicular, ovulatory and luteal, and relevant periods of transformation of mucous membrane of the uterus (endometrium) – menstrual, proliferative and secretory.
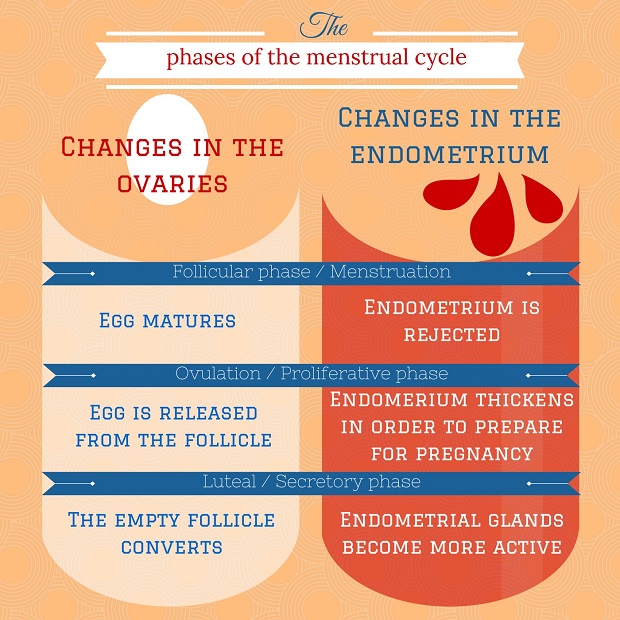
During the first phase the “parade is lead” by the follicle-stimulating hormone. It prepares the ovum for the detachment from the follicle, but at this moment female reproductive organs are not disposed to pregnancy. Menstruation occurs in the beginning of the phase, which is followed by the “dry vagina” period, when there is almost no discharge.
Once estrogen comes to power, the amount of mucus starts increasing steadily. At first it is not abundant, but thickish and sticky. However, over some time the situation changes drastically. During the proliferative phase, i.e. before and during ovulation, there is quite a lot of mucus, it is fluid and can be easily stretched between fingers.
At the beginning of the third phase, the leading role belongs to lutein and its successor – progesterone. Endometrium actively secretes, preparing itself for the ovum. In case pregnancy does not take place, the level of these hormones reduces and the discharge becomes more and more scant.
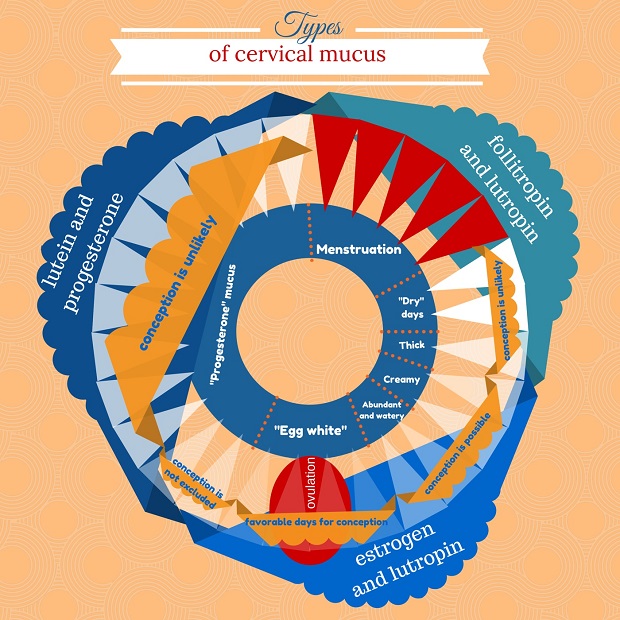
Types of cervical mucus
In fact apart from cervical mucus after implantation, we distinguish between five possible forms of discharge:
- «Dry» days – there is practically no discharge;
- Thick, sticky mucus, hardly favorable for sperm cells;
- Creamy-like secrete – chances of fertilization increase;
- Abundant fluid discharge – fertilization is highly probable;
- Abundance of mucus, which externally resembles an egg white. It stretches well, when collected from vagina with a finger.
The following mucus tests are conducted in laboratory conditions. A sample of cervical discharge is applied on a glass slide, and once dried up, it is examined under the microscope. The “fetal” CM (from a creamy-like to an egg white) has a specific appearance, resembling a frond. Such a picture is observed from 7 to 18 days of the ovulatory menstrual cycle. It has to do with a high content of sodium chloride in the secrete, which is conditioned by the influence of estrogen. As the salt content reduces after the 21st day, mucus becomes thicker and cloudy, and the “frond” image is nor formed.
Cervical method of birth control
It is believed that regular observation of the CM nature and maintenance of a relevant register can help in “calculating” favorable and unfavorable days for fertilization. For this purpose, it is required to test the presence and consistency of mucus with the help of a clean finger, putting it into vagina and entering one of the 5 relevant definitions in your diagram.
In practice, this method didn’t prove to be accurate – 15 women out of 100, who use this method of contraception, get pregnant. The reasons are as follows:
- Individual fluctuations in the hormonal level provoke the discharge of “egg white” type of CM before ovulation, due to which the woman considers that the ovum has already been detached and thus, stops bewaring of an unprotected intercourse;
- Peculiarities of secretion in the form of constant and steady discharge of homogeneous mucus;
- Impossibility of application of this method and its adequate evaluation for women with vaginal and uterine diseases.
Apart from this, there can be diagnostic inaccuracies in case the CM examination is carried out immediately before the coitus (mucus is lavishly doped with lubrication) or after it, as for several hours after the intercourse the mucus will be missed with the sperms cells.
Cervical mucus after conception
Implantation takes place when the ovum adheres to the endometrium and invades it later on. The woman’s organism undergoes complete alteration, primarily hormonal. Thus, from now on and up to delivery all the endocrine processes are governed by the “pregnancy hormone” – progesterone. It stimulates a better blood supply and swelling of the uterine cervix, enlargement and proliferation of its glands. For a few days the cervical pharynx is plugged with a thick mucus layer. It has to do with the fact that CM has already performed its key function of unification. Now it only has to maintain mechanical protection of the developing organism.
During a clinical test, when CM after implantation is dried up on a glass side, it will only show up fragmentary crystallization, which will be the result of obvious influence of progesterone.
Increase of hormonal activity in the first trimester of pregnancy may result in abundant fluid discharge. However, most often, there is little mucus and it is rather thick. In any case, the only thing that should be paid attention to is the presence of any infections. The following factors can be indicative to their existence:
- Green, yellow or dim-grey color of discharge;
- Unpleasant smell;
- Secretion, accompanied by itchiness, etc.
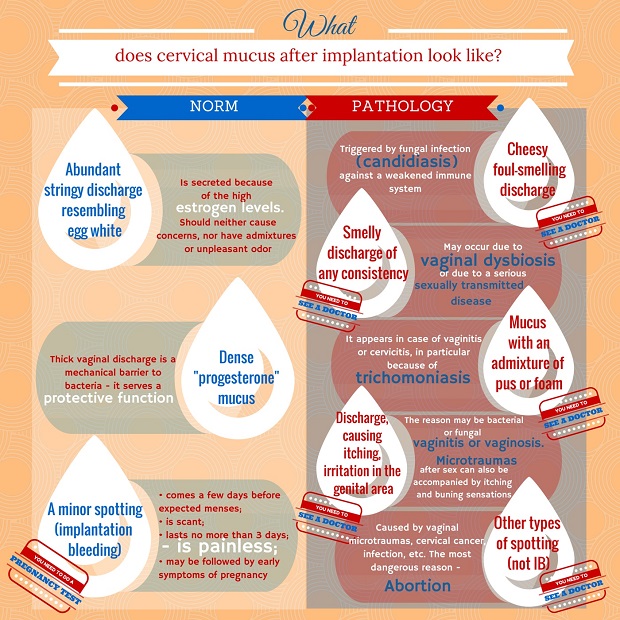
Any of these symptoms, as well as presence of blood in the discharge, should put you on alert and serve ground for a visit to a doctor. In case the implantation discharge is transparent or white, has normal consistency and does not have a specific smell – then there is no reason for worrying. You should just maintain proper hygiene and enjoy the wonderful stage of your life – carrying a baby.